| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
- Swift 고차함수
- 2022 부스트캠프
- 스위프트 클로저
- Associated Value
- iOS Static Library 사용하는방법
- leetcode #01
- Swift
- 일급 객체
- 트레일링 클로저
- CoreData
- Swift LinkedList
- Swift closure
- dateFormatter
- Raw value and Associated value
- 1009번
- Persistent store Coordinator
- CoreData Stack
- NSSortDescriptor
- 다익스트라 이해
- CoreData Concurrency
- Clean swift
- persistentStoreCoordinator
- Java
- expensive operation
- codability
- NSPredicates
- iOS Static Library
- NSManagedObject SubClass
- LightWeight Migration
- CoreData Filter
- Today
- Total
하루를살자
Swift - Collection Types 본문
Collection Types
Swift 는 collection 의 값들을 저장하는 3가지의 기본 collection type 을 가지고 있다.
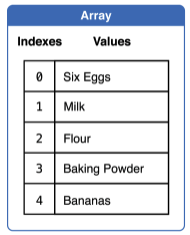
1. Arrays
--> Collection 의 값들이 순서 있게 저장됨.
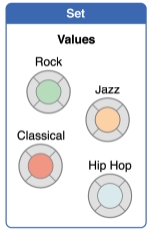
2. Sets
--> 유니크 한 collection 값들이 순서 없이 저장됨.
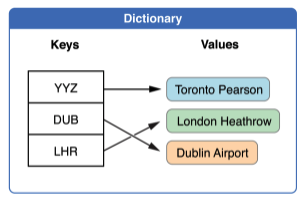
3. Dictionary
--> Key-Value 로 되어있는 collection 들이 순서 없이 저장됨.
- 위의 3가지 타입들은 Swift 에서 저장 할수 있는 값들의 의 타입과 key 에 대해서 민감하다. 이는, 잘못된 타입을 collection 에 넣는것을 방지해주고, 사용자가 항상 어떤 타입의 값들을 해당 collection 에서 받을지, 넣어줄지 확신 할수 있게 해준다.
Mutability of Collections
- 위의 3가지 타입들을 생성하고 어떠한 변수에 지정을 해주면, 그 collection 은 변할수 있는 상태가 된다 (mutable). 즉 사용자는 해당 collection 의 내용에 값을 넣고, 지우고 바꿀수 있다는 뜻이다. 그 반대로, 만약 사용자가 변할수 없는 상태로 (immutable) 변수에 지정한다면, 해당 collection 의 내용과 크기는 변할수 없게 된다.
*Note
Immutable 한 collection 을 수정이 필요하지 않는 collection 에 항상 지정해주는 연습을 하면 자신이 쓴 코드에 대해 타당한 이유 를 들수 있고, Swift 컴파일러가 생성된 collection 의 퍼포먼스를 최적화할수 있게 해준다.
Arrays
Creating an empty Array
var someInts: [Int] = []
//Note that the type of the someInts variable is inferred tobe [Int] from the type
//of the initializerCreating an Array with a Default Value
Swift 의 array 는 기본적으로 크기와 같은 값을 넣어주는 initializer 가 아래와 같이 존재한다.
var threeDoubles = Array(repeating: 0.0, count:3)
// threeDoubles is of type [Double], and equals [0.0 , 0.0, 0.0]Creating an Array by Adding Two Arrays Together
만약 같은 타입의 배열들이 있다면, + operator 를 사용해서 새로운 배열을 생성할수있다.
var anotherThreeDoubles = Array(repeating: 2.5, count: 3)
// anotherThreeDoubles is of type [Double], and equals [2.5, 2.5, 2.5]
var sixDoubles = threeDoubles + anotherThreeDoubles
// sixDoubles is inferred as [Double], and equals [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 2.5, 2.5, 2.5]Accessing and modifying an Array
1. 배열 안의 요소 갯수 = .count
2.빈 배열 확인법 = .isEmpty
3. 배열안에 새로운 요소 넣기 = .append / +=
4. 특정 범위 안의 배열요소 바꾸기 = Array[Int...Int+N] = ["item1", "item2"]
5. 특정 인덱스에 요소 넣기 = Array.insert("item", at: Int)
6. 특정 인덱스 요소 삭제 = Array.remove(at : Int)
Iterating Over an Array
배열의 인덱스와 값을 둘다 필요할경우레, enumerated() 메소드를 사용할수있다.
각각의 배열의 요소들에대해서 enumerated() 메소드는 Integer 와 Item 을 갖는 tuple 을 리턴해 주고 아래와 같이 쓰일수있다.
for (index, value) in Array.enumerated(){
print ("\(index) : \(value)")
}Sets
Set 은 같은 타입의 유니크한 값을 순서 없이 저장한다. 보통 set 은 순서가 중요하지않는 데이터를 다룰때 쓰이고, 특정한 값이 들어가기 때문에 그 특정값이 한번만 들어기 원할때 쓰일수 있다.
Hash Values for Set Types
Set 에 들어갈 값의 타입들은 반드시 hashable 해야한다. 이말은, 그 타입이 hash 값을 가질수 있어야한다는 뜻이다. Hash 값은 모든 object 들이 동등하게 비교되는 정수형 이고, 만약 a 가 b 와 같다면, 그 a 의 hash 값 은 b의 hash 값과 같다.
모든 swift 의 기본 타입 (String, Int, Dobule, and Bool) 들은 기본적으로 hashable 하고 set 의 Value 또는 Key 에 사용될수 있다.
*Associated Value 가 없는 열거형도 기본적으로 hashable 하다
Set Syntax
--> Set<Element>
where Element is the type that the set is allowed to store
Creating and Initializing an Empty Set
var letters = Set<Character> ()
print ("Letters is of type Set<Character> with \(letters.count) items")
// -> 0 items
letters.insert("a")
// letters now contains 1 value of type Character
letters = []
// letters is now an empty set, but is still of type Set<Character>
var favoriteGenres: Set<String> = ["Rock", "Classical", "Hip hop"]
// favoriteGenres has been initialized with three initial itemsfavoriteGenres 에서 String 타입의 Set 으로 3개의 값 "Rock", "Classical", "Hip hop" 이 선언 됨.
Accessing and modifying Sets
Set 메소드와 perperties 를 사용하여 아래와 같이 값에 접근 할수 있다. (배열과 비슷함)
1. Set 의 요소 갯수 = Set.count
2. Set이 비어있는지 확인 = Set.isEmpty
3. Set에 값 넣기 = Set.insert("item")
4. Set 의 요소 지우기 = Set.remove("item")
5. Set 의 요소가 특정한 값을 가지고 있는지 확인 = Set.contains("item")
Iterating over a set
//for - in loop
for genre in favoriteGenres {
print("\(genre)")
}
//sorting the elements
for genre in favoriteGenres.sorted() {
print("\(genre)")
}
// Classical
// Hip hop
// Jazz
Performing Set Operations
Set 에는 효율적인 몇가지 기능들이 있다.
1. 공통 집합 = intersection()
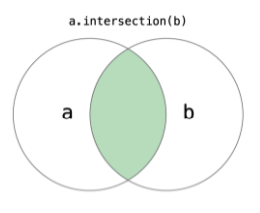
2.대칭 집합 = symmetricDifference()
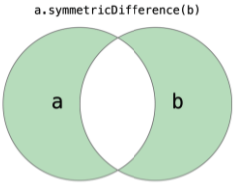
3. 합집합 = union()
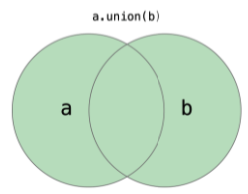
4. 차집합 = subtracting()
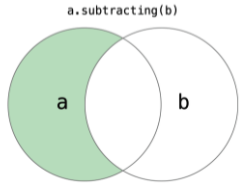
//홀수
let oddDigits: Set = [1, 3, 5, 7, 9]
//짝수
let evenDigits: Set = [0, 2, 4, 6, 8]
//소수
let singleDigitPrimeNumbers: Set = [2, 3, 5, 7]
oddDigits.union(evenDigits).sorted()
// [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
oddDigits.intersection(evenDigits).sorted()
// []
oddDigits.subtracting(singleDigitPrimeNumbers).sorted()
// [1, 9]
oddDigits.symmetricDifference(singleDigitPrimeNumbers).sorted()
// [1, 2, 9]Set Membership and Equality
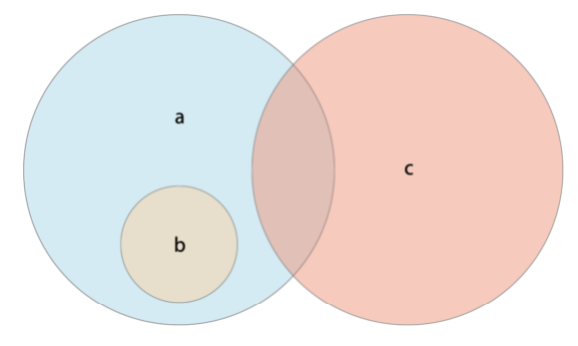
1. a 는 b의 상위집합이다.
2. b는 a 의 부분 집합이다.
3. b 와 c 는 서로 disjoint 한다.
let houseAnimals: Set = ["🐶", "🐱"]
let farmAnimals: Set = ["🐮", "🐔", "🐑", "🐶", "🐱"]
let cityAnimals: Set = ["🐦", "🐭"]
houseAnimals.isSubset(of: farmAnimals)
// true
farmAnimals.isSuperset(of: houseAnimals)
// true
farmAnimals.isDisjoint(with: cityAnimals)
// trueDictionaries
Dictionary 는 Key 와 Value 를 같고 순서가 없다. 각가의 값은 유니크한 key 와 연동되어 있다.
Set과 마찬가지로 dictionary 의 Key 값은 hashable 해야한다.
Creating Dictionary
//Creating an empty [Int: String] dictionary
var namesOfIntegers :[Int: String] = [:]
namesOfIntegers[16] = "Sixteen"
//it now contains 1 key-value pair
namesOfInteger = [:]
//it is now empty
//Creating Dictionary with literal
var airports: [String: String] = ["YYZ": "Toronto Pearson", "DUB": "Dublin"]
//It can be also written as below
var airports = ["YYZ": "Toronto Pearson", "DUB": "Dublin"]
Accessing and modifying a dictionary
// 1. Counting
print("The airports dictionary contains \(airports.count) items.")
// Prints "The airports dictionary contains 2 items."
// 2. Checking if its empty
if airports.isEmpty {
print("The airports dictionary is empty.")
} else {
print("The airports dictionary isn't empty.")
}
// Prints "The airports dictionary isn't empty."
// 3. adding new item
airports["LHR"] = "London"
// 4. changing dictionary
airports["LHR"] = "London Heathrow"
//or
airports.updateValue("London Heathrow", forKey:"LHR")
// 5.Checking if the interested Key exists within the dictionary and update
if let oldValue = airports.updateValue("Dublin Airport", forKey: "DUB") {
print("The old value for DUB was \(oldValue).")
}
// Prints "The old value for DUB was Dublin.
// 6. subscript syntax 를 사용하여 값 받기
if let airportName = airports["DUB"] {
print("The name of the airport is \(airportName).")
} else {
print("That airport isn't in the airports dictionary.")
}
// Prints "The name of the airport is Dublin Airport."
// 7. nil 사용하여 지우기
airports["APL"] = "Apple International"
// "Apple International" isn't the real airport for APL, so delete it
airports["APL"] = nil
// APL has now been removed from the dictionary
// 8. removeValue 사용 하여 요소 지우기. 5번과 같은 맥락임 .
if let removedValue = airports.removeValue(forKey: "DUB") {
print("The removed airport's name is \(removedValue).")
} else {
print("The airports dictionary doesn't contain a value for DUB.")
}
// Prints "The removed airport's name is Dublin Airport."5 번의 optional binding 에서 upDateValue 의 키값의 value 가 존재할경우 업데이트 이전에 oldValue 로 값을 리턴해주고 만약 이전 값이 존재하지 않을경우 nil 리턴. 같은 맥락으로
Iterating Over a dictionary
for (airportCode, airportName) in airports {
print("\(airportCode): \(airportName)")
}
//key 와 value 으로 for in loop
for airportCode in airports.keys{
print(airportCode)
}
for airportName in airports.values {
print(airportName)
}
//만약 Array 형태로 Key 나 Value 값을 저장하고 싶다면
let airportCodes = [String](airports.keys)
// airportCodes is ["LHR", "YYZ"]
let airportNames = [String](airports.values)
// airportNames is ["London Heathrow", "Toronto Pearson"]Dictionary 는 순서 없이 값을 저장 하기떄문에 key, 나 value 에 sorted 메소드를 사용해서 원하는 순서를 정할수 있음.
'Swift' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Swift - Closure (1): 표현식 (0) | 2022.02.27 |
|---|---|
| Swift 고차함수 (0) | 2022.02.05 |
| Swift - Enum (0) | 2021.12.31 |
| Swift - Optionals (0) | 2021.12.21 |
| SwiftUI Architecture - MVVM (Model, View, and ViewModel) (0) | 2021.12.20 |